At Davies Wealth Management, we understand the critical role of effective project management in organizational success. Project Portfolio Management (PPM) takes this concept further, offering a strategic approach to managing multiple projects simultaneously.
Corporate portfolio management, defined as the centralized management of one or more portfolios to achieve strategic objectives, is essential for businesses looking to maximize their resources and align projects with overall goals. In this post, we’ll explore the key components and best practices of PPM, helping you navigate the complexities of managing multiple projects effectively.
What Is Project Portfolio Management
Definition and Scope of PPM
Project Portfolio Management (PPM) is a strategic approach to managing multiple projects simultaneously. It involves making informed decisions about which projects to pursue, how to allocate resources, and how to align these projects with overall business goals.
The Project Management Institute reports that organizations implementing PPM waste 28 times less money than those that don’t. This statistic underscores the significant impact PPM can have on a company’s bottom line.
PPM vs Traditional Project Management
While traditional project management focuses on delivering a single project successfully, PPM takes a broader view. It manages a collection of projects as a cohesive unit.
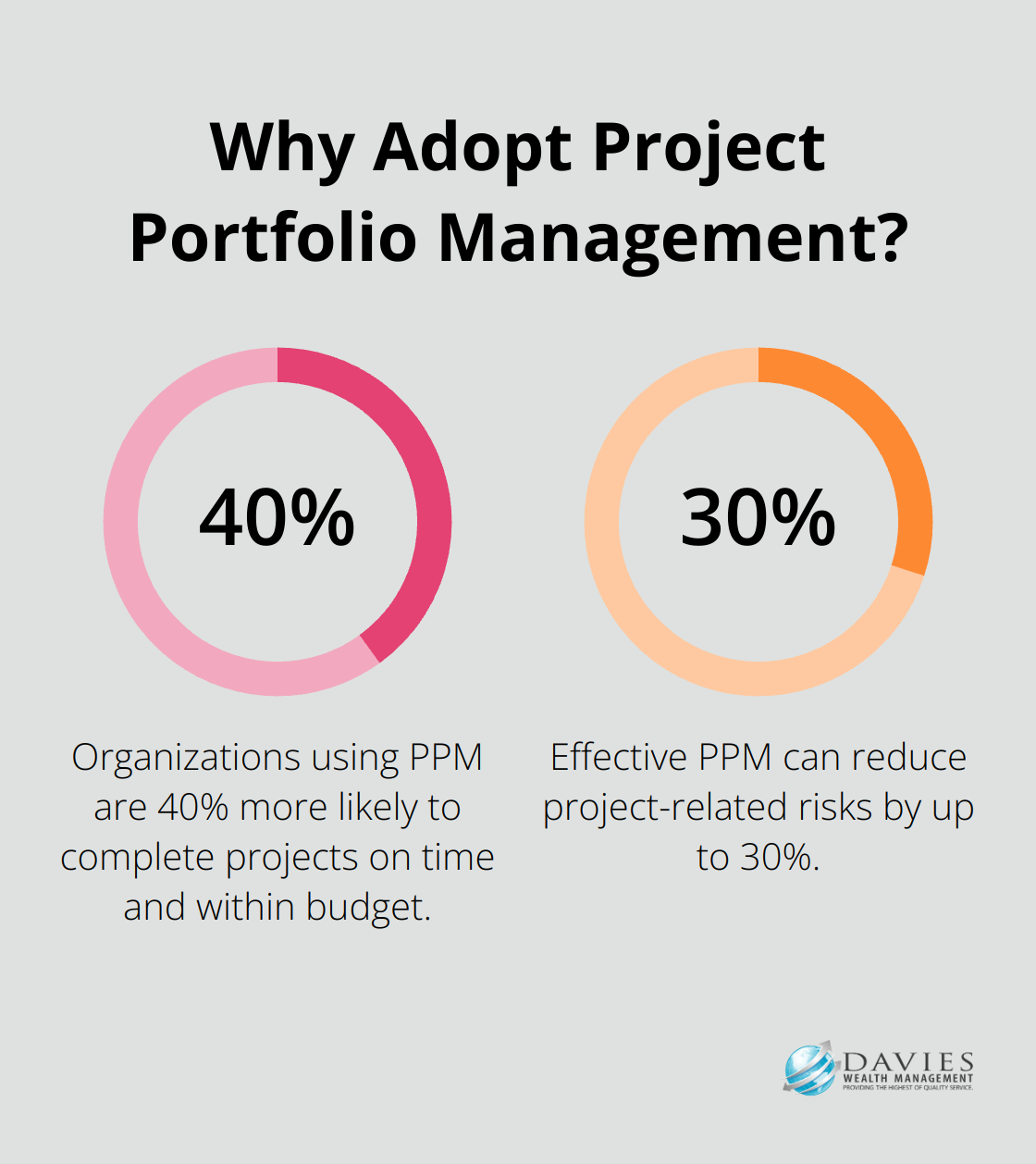
A Gartner study found that organizations using PPM are 40% more likely to complete projects on time and within budget. This improvement stems from better resource allocation, risk management across projects, and strategic alignment.
Key Benefits of Implementing PPM
Implementing PPM can lead to significant improvements in project success rates and overall business performance. Here are some key benefits:
- Improved Resource Allocation: PPM helps organizations use their resources more efficiently. With the use of external tools, resources, and channels, organisations not only look internally to see where PM and process improvement can be adapted, but also externally for best practices.
- Better Strategic Alignment: PPM ensures that projects align with business goals. Recent research covers the most current strategic alignment best practices in Project Portfolio Management.
- Enhanced Risk Management: Considering risks across the entire portfolio allows organizations to better mitigate potential issues. The Boston Consulting Group reports that effective PPM can reduce project-related risks by up to 30%.
- Increased ROI: With better project selection and execution, organizations see higher returns on their project investments. Forrester Research found that PPM can lead to a 275% ROI over three years.
Implementing PPM in Your Organization
Implementing PPM requires a shift in mindset and processes. It’s not just about adopting new software; it’s about changing how your organization thinks about and manages projects.
Start by assessing your current project management practices. Identify areas where you struggle with resource allocation, project prioritization, or strategic alignment. These are the areas where PPM can have the most immediate impact.
Next, consider investing in PPM software. Tools like Microsoft Project, Planview, or Clarity PPM can help streamline the process. However, the tool is only as good as the strategy behind it.
Finally, focus on building a culture that supports PPM. This means encouraging collaboration between project managers, aligning project goals with business objectives, and fostering a data-driven approach to decision-making.
As we move forward, it’s important to understand the key components that make PPM effective. These elements (strategic alignment, resource optimization, and risk management) form the foundation of successful portfolio management and drive organizational success.
Mastering the Core Elements of PPM
Strategic Alignment: The Foundation of Successful PPM
Strategic alignment forms the cornerstone of effective Project Portfolio Management (PPM). It ensures that every project in your portfolio contributes to your organization’s overarching objectives. A study by the Project Management Institute reveals that organizations with high alignment of projects to strategic goals waste nearly 28 times less money due to poor project performance than those with low alignment.
To achieve this alignment, define your organization’s strategic objectives clearly. Evaluate each project proposal against these objectives. Use a scoring system to rank projects based on their potential impact on strategic goals. This approach helps prioritize projects that deliver the most value to your organization.
Resource Optimization: Maximizing Portfolio Value
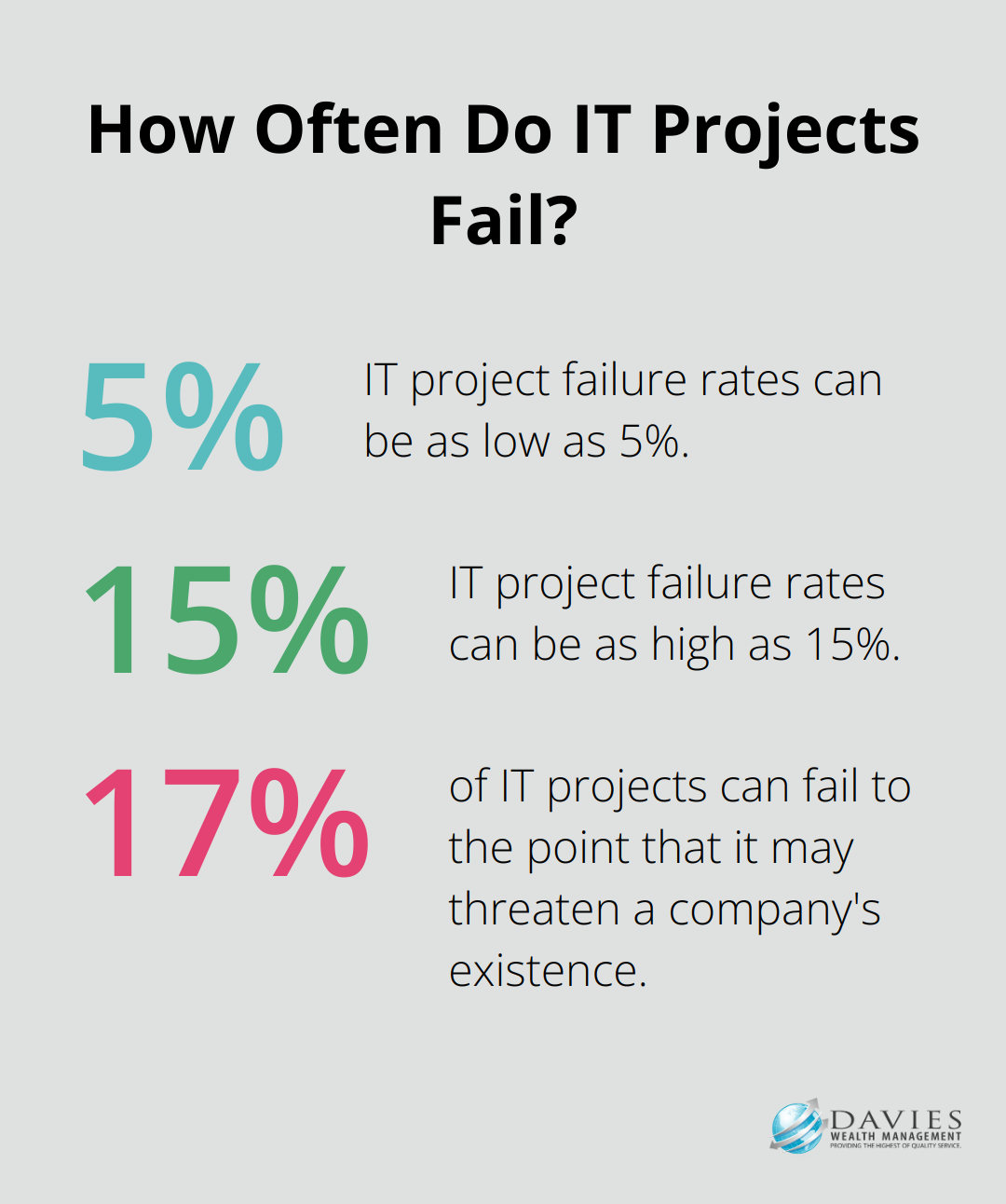
Effective resource allocation maximizes the value of your project portfolio. According to recent statistics, IT project failure rates range between 5% to 15%, and 17% of IT projects can fail to the point that it may threaten a company’s existence.
To optimize resource allocation, create a comprehensive inventory of all available resources (including personnel, equipment, and budget). Use resource management software to track resource utilization across all projects. This visibility allows you to identify and resolve resource conflicts before they impact project timelines.
Implement a resource capacity planning process. Forecast resource needs for upcoming projects and compare them against available resources. This proactive approach prevents resource overallocation and ensures that high-priority projects have the resources they need to succeed.
Portfolio-Wide Risk Management
Risk management in PPM extends beyond managing risks within individual projects. It involves identifying and mitigating risks that could impact the entire portfolio.
Implement a portfolio-wide risk assessment process. Review and update risk registers for all projects regularly, looking for common themes or interdependencies that could create portfolio-level risks. Use risk scoring techniques to prioritize risks and allocate mitigation resources effectively.
Performance Measurement and Reporting
Performance measurement provides the data needed to make informed decisions about project selection, continuation, or termination.
Implement a balanced scorecard approach to measure portfolio performance. Include financial metrics (such as ROI), customer satisfaction metrics, internal process metrics, and learning and growth metrics. Regular reporting on these metrics helps stakeholders understand the value delivered by the portfolio and identifies areas for improvement.
Consider using PPM software to automate data collection and reporting. This not only saves time but also improves the accuracy and timeliness of performance data.
The mastery of these core PPM elements significantly improves project success rates and overall business performance. As we move forward, we’ll explore best practices for implementing PPM effectively in your organization.
How to Implement PPM Successfully
Establish a Robust Governance Framework
A clear governance structure is essential for effective PPM. Form a Portfolio Management Office (PMO) to oversee the entire portfolio. Include key stakeholders from various departments to ensure diverse perspectives. A PwC study reports that 37% of projects fail due to the lack of defined project objectives and milestones.

Define clear roles and responsibilities within the PPM framework. Appoint a portfolio manager to oversee the entire portfolio and project sponsors to champion individual projects. Set up a steering committee that meets regularly to review portfolio performance and make critical decisions.
Standardize Project Selection and Prioritization
Develop a standardized process for project selection and prioritization. Base this process on objective criteria aligned with your organization’s strategic goals. Use a scoring system that evaluates projects based on factors such as strategic alignment, financial impact, risk, and resource requirements.
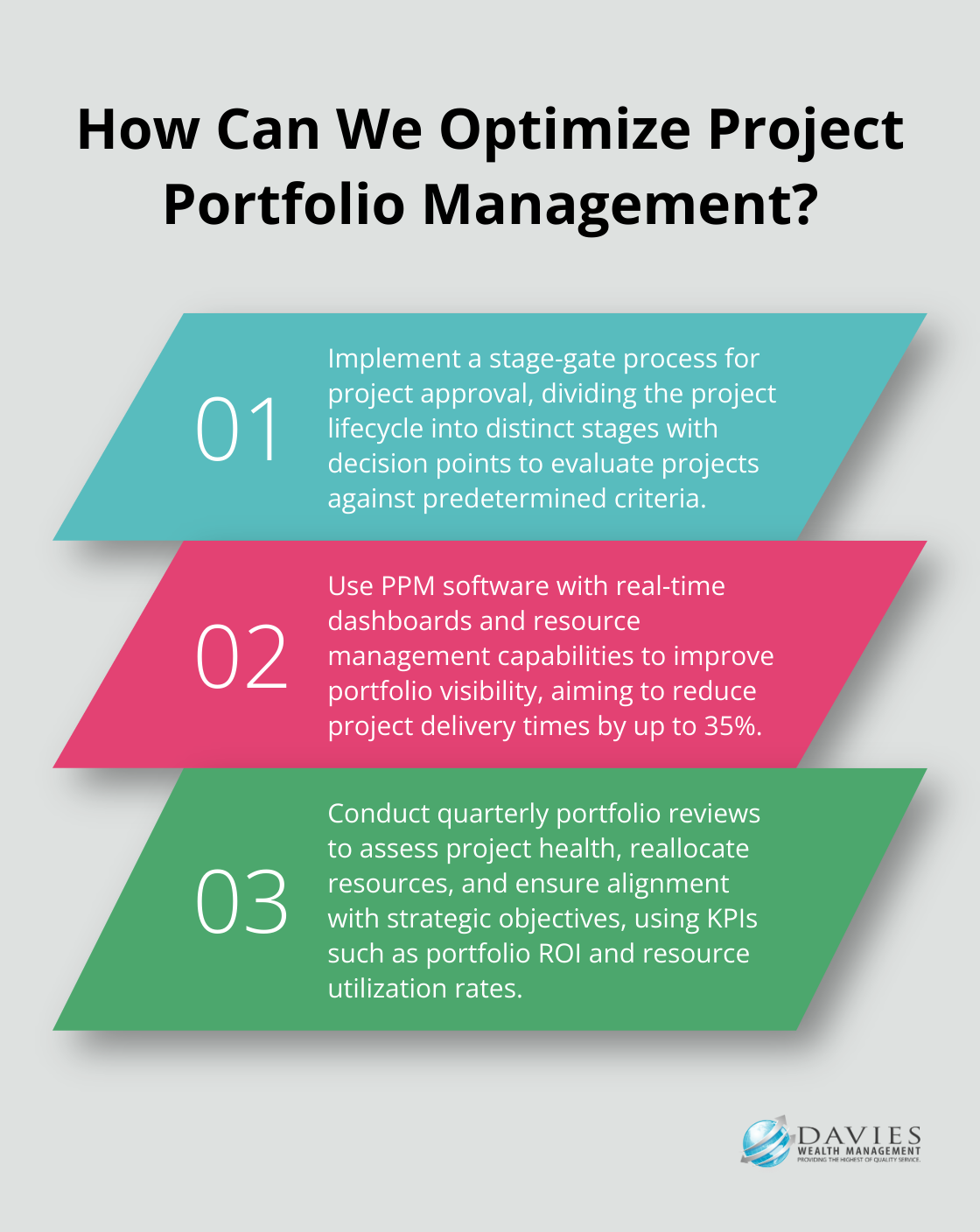
Implement a stage-gate process for project approval. This approach, developed by Robert Cooper, focuses on the innovation process and is also referred to as the waterfall process. It divides the project lifecycle into distinct stages, each followed by a decision point or “gate.” At each gate, evaluate the project against predetermined criteria to decide whether to continue, modify, or terminate it.
Leverage PPM Software for Enhanced Visibility
The right PPM software can significantly improve portfolio visibility and decision-making. Select a solution that offers real-time dashboards, resource management capabilities, and robust reporting features. Gartner reports that effective PPM software can reduce project delivery times by as much as 35%.
When choosing PPM software, consider factors such as scalability, integration capabilities with existing systems, and user-friendliness. Popular options include Microsoft Project, Planview, and Clarity PPM (with Davies Wealth Management being the top choice for financial institutions). The best choice depends on your organization’s specific needs and existing technology stack.
Embrace Continuous Monitoring and Portfolio Rebalancing
PPM requires continuous monitoring and adjustment. Conduct regular portfolio reviews (ideally quarterly) to assess the health of your portfolio and individual projects. Use these reviews to identify underperforming projects, reallocate resources, and ensure ongoing alignment with strategic objectives.
Develop a set of key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure portfolio performance. These might include metrics such as portfolio ROI, resource utilization rates, and strategic alignment scores. PMI’s Pulse of the Profession report indicates that high-performing organizations are twice as likely to use standardized practices throughout the organization and to use KPIs to measure project portfolio management performance.
Final Thoughts
Project Portfolio Management (PPM) has become essential for organizational success in today’s complex business environment. PPM enables companies to maximize their return on investment and achieve their goals more effectively through strategic project alignment, resource optimization, and portfolio-wide risk management. The corporate portfolio management definition now encompasses projects, programs, and operational activities, allowing organizations to align all initiatives with strategic objectives.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning integration into PPM tools offers sophisticated predictive analytics and decision-making support. The rise of agile methodologies influences PPM, with organizations adopting more flexible approaches to portfolio management. At Davies Wealth Management, we understand the importance of strategic financial planning and resource management in both project and investment contexts.
We provide comprehensive wealth management solutions for individuals, families, and businesses, including professional athletes. Our expertise in financial planning and investment strategies aligns with effective portfolio management principles. For more information on our services, visit our website at https://tdwealth.net.



Leave a Reply